Learning Geology What Drives Plate Motion, and How Fast Do Plates Move?
Although ridge-push/slab-pull is the widely favoured mechanism for plate motion, it's important not to underestimate the role of mantle convection. Without convection, there would be no ridges to push from because upward convection brings hot buoyant rock to surface.
PPT Plate Tectonics II PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1442286
ridge push and slab pull , are more important. Some argue that the real answer lies somewhere in between. To understand mantle convection , imagine a pot of water on a hot stove. The water at the bottom of the pot near the heat source becomes hot and expands, making it lighter (less dense) than the water above.

Tectonic Boundaries by Shelby Harrison
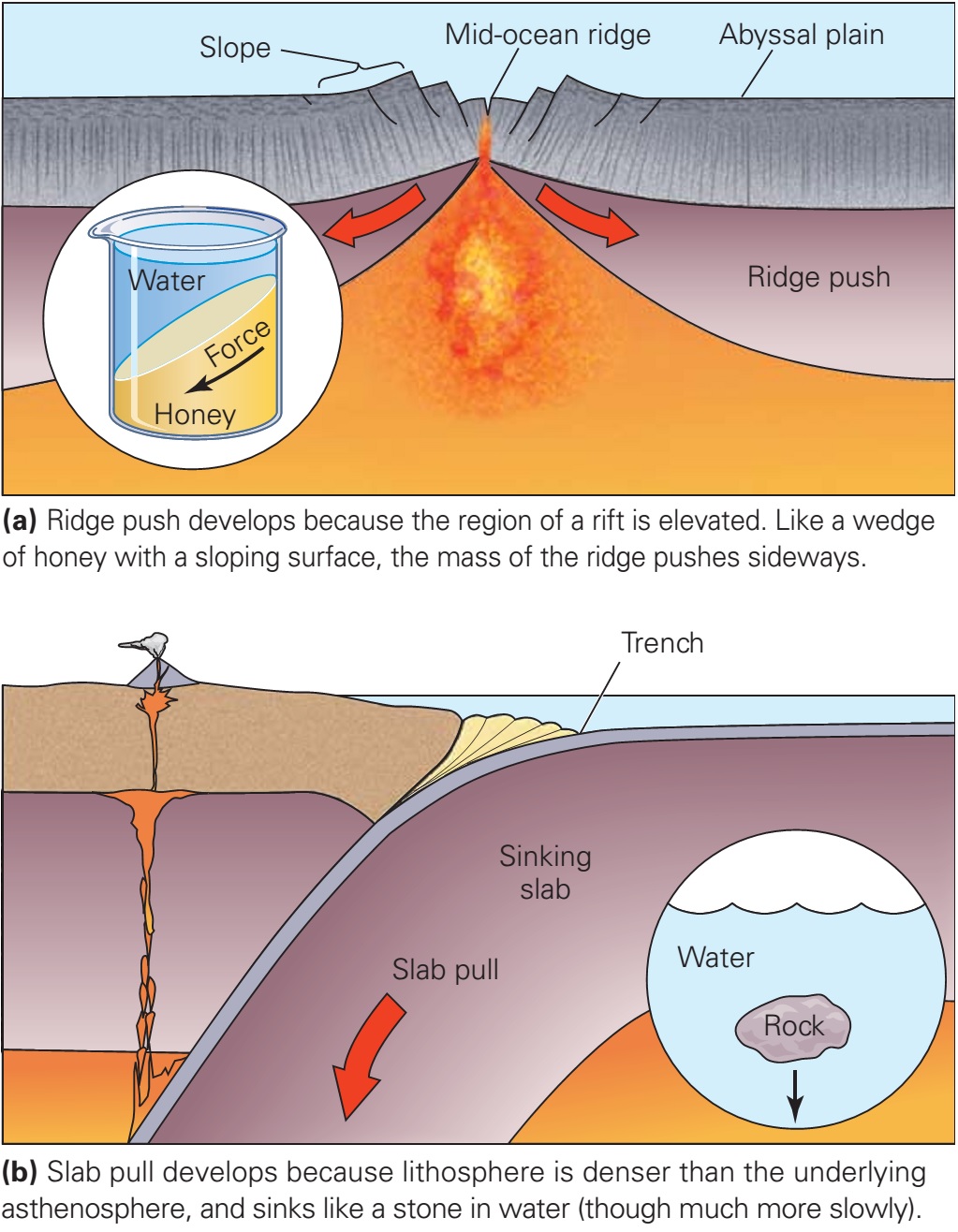
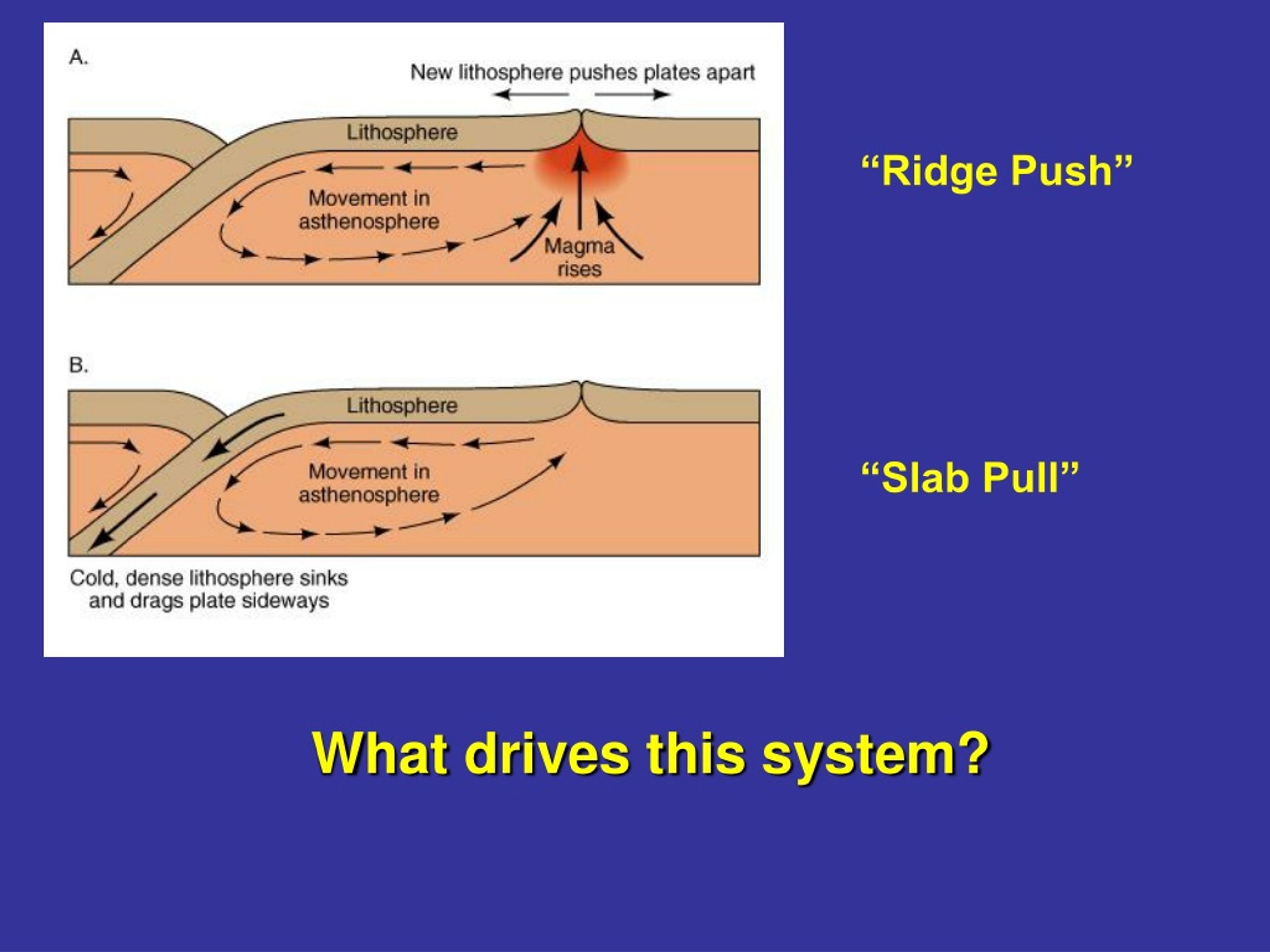
Ridge Push: The pressure exerted by the excess height of the mid-ocean ridge. Introduction The history of the development of plate tectonics is centrally tied to the question of what drives plate motions.
PPT Geol 351 Geomath PowerPoint Presentation ID6745991
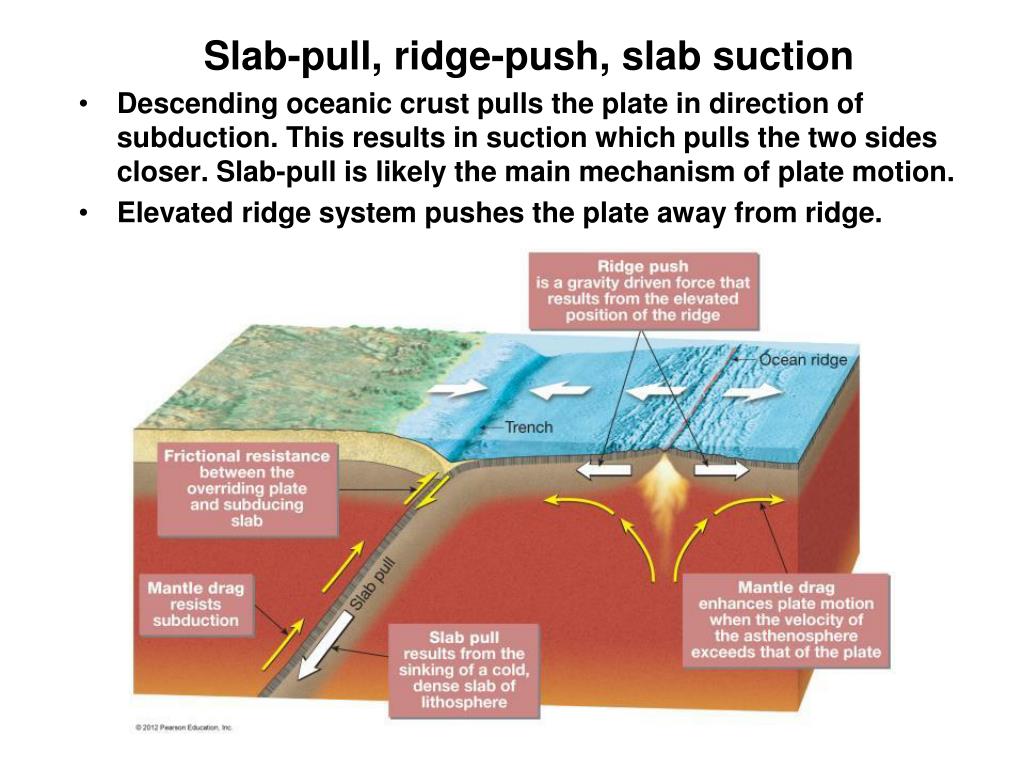
Driving Forces: Slab Pull, Ridge Push Carolina Lithgow-Bertelloni* Department of Earth Sciences, University College London, London, UK Definition Plate Driving Forces: The forces that drive the motions of tectonic plates at the surface. Slab Pull: The force exerted by the weight of the subducted slab on the plate it is attached to.
PPT Chapter 4 Section 3 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID152668
Ridge push is thought responsible for the motion of these plates. The subducting slabs around the Pacific Ring of Fire cool down the Earth and its core-mantle boundary. Around the African Plate upwelling mantle plumes from the core-mantle boundary produce rifting including the African and Ethiopian rift valleys. See also Mid-ocean ridge

Tectonic Hazards Revision Cards in GCSE Geography
What is the difference between slab pull and ridge push? The difference between slab pull and ridge push is where they occur along an oceanic plate, and how much they contribute to the.

Plate Tectonics by Brianna Wildroudt
Figure 10.5.2 10.5. 2 The ridge-push/slab-pull model for plate motion, in which the lithosphere is the upper surface of the convective systems. Although ridge-push/slab-pull is the widely favoured mechanism for plate motion, it's important not to underestimate the role of mantle convection. Without convection, there would be no ridges to push.

Plate Tectonics by Caitlin Dems
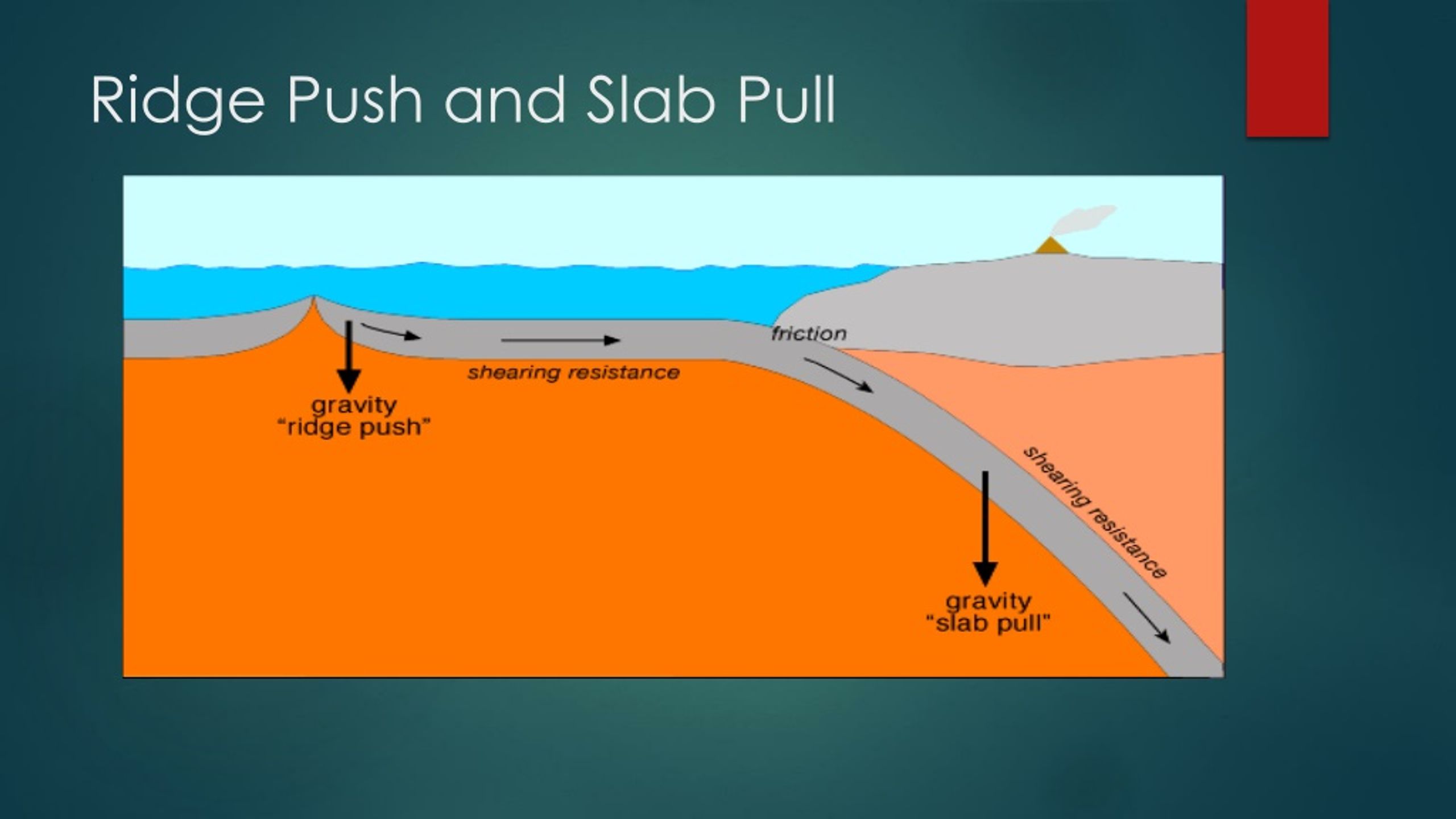
"slab pull" As lithospheric plates move away from midocean ridges they cool and become denser. They eventually become more dense than the underlying hot mantle. After subducted, cool, dense lithosphere sinks into the mantle under its own weight. This helps to pull the rest of the plate down with it.

Plate Tectonics by Jessica Loos
Ridge push occurs because the ridge is at a higher elevation than the surrounding topography. This creates a slope that the plate can then slide downward on. Overview of Plate Tectonics Plate.

Ridge Push Slab Pull
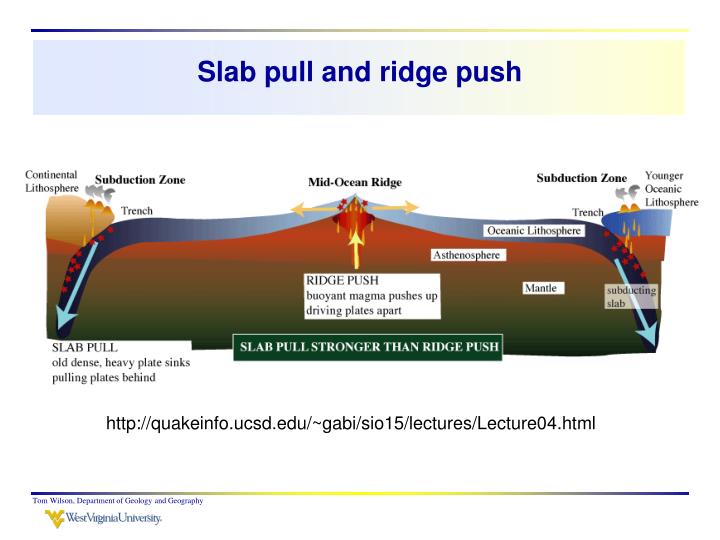
The ridge push/slab pull model also relies on mantle convection, but in this case it is not simply the traction from the convection cell that moves the plates. In this model, plates move through a combination of pull from the weight of the subducting edge of the plates, and through the outward pushing of an ocean ridge where magma is rising and forming new crust (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)).

Plate Tectonics by Caitlin Dems
Slab pull Ridge push Gravitational sliding Gravitational forces Plate tectonics More recent theories of plate movement consider the effect of gravitational forces acting within the crust that also contribute to plate movement, although the impact is thought to be weaker than the effect of convectional movement in the mantle.

Ridge Push, Slab Pull or Trench Suction Labeled Scheme Vector Illustration. Stock Vector
Ridge push and slab pull is now the more widely accepted theory. Ocean ridges form high above the ocean floor at constructive margins (where the plates are moving away from each other). Here the mantle melts to form molten magma which rises as the plates move apart and then cools to form new oceanic lithosphere.
PPT Divergent Boundary PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9170975
Ridge push (also known as gravitational sliding or sliding plate force) is a proposed driving force for plate motion in plate tectonics that occurs at mid-ocean ridges as the result of the rigid lithosphere sliding down the hot, raised asthenosphere below mid-ocean ridges.

Plate tectonics Continental Drift, Subduction, Earthquakes Britannica
The energy source for plate tectonics is Earth's internal heat while the forces moving the plates are the "ridge push" and "slab pull" gravity forces. It was once thought that mantle convection could drive plate motions.

Ridge push slab pull YouTube
slab pull and ridge push are believed to move the tectonic plates. Ridge push is where the new crust formed at divergent plate margins is less dense than the surrounding crust and so it.

Construct and label a model that shows the processes of ridg Quizlet
Slab-Pull Force; Ridge-Push Force; The motion of tectonic plates is driven by convection in the mantle. In simple terms, convection is the idea that dense, cold things sink, and buoyant, warm things rise. In the earth the cold sinking things are slabs (subducting plates) and the warm things are plumes, or just rising material from deeper in the.